Earth Observation Satellites
Project
Development of a new approach to evaluate satellite derived XCO2 over oceans by integrating commercial ship and aircraft observations
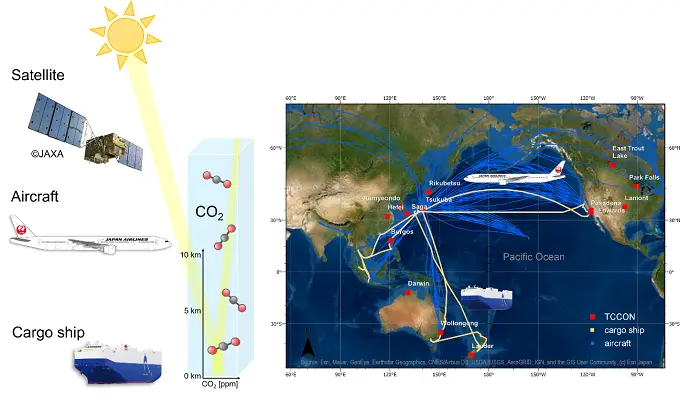
In our group at the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), we developed a new method to evaluate satellite observations of column-averaged mixing ratios of carbon dioxide (XCO2) over open ocean areas, which are currently inaccessible through established validation network sites. In the new approach, a reference XCO2 dataset is formulated by combining cargo ship and passenger aircraft observations which were conducted in cooperation with operators of the private sector.
High quality satellite observations are a requirement for better understanding of the carbon cycle in response to climate change. However, satellite derived XCO2 show greater biases apparently over oceans than over the land surface. Advances in retrieval algorithms are made rapidly. But up to date, no effective ways to evaluate these improvements and the space-time XCO2 variations over open oceans exist.
Our team expect that the new observation based XCO2 (obs. XCO2) dataset contributes to the further improvements of satellite data in regions where no reference data are available as complement to established validation networks. With our approach, the temporal and spatial coverage of obs. XCO2 can be rapidly and cost-efficiently extended through the help of the private sector. In future, our new method will be applied to other important trace gases.